This is project to bootstrap the creation of domain-specific datasets for training models. The goal is to create a set of tools that help users to collaborate with domain experts.
LLMs are increasingly used as economical alternatives to human participants across various domains such as computational social science, user testing, annotation tasks, and opinion surveys. However, the utility of LLMs in replicating specific human nuances and expertises is limited by inherent training constraints. Models are trained on large-scale datasets that are often biased, incomplete, or unrepresentative of the diverse human experiences they aim to replicate. This problems impacts specific expert domains like as well as underrepresented groups in the training data.
Also, building synthetic datasets that are representative of the domain can help to improve the performance of models in the domain.
The goal of this project is to share and collaborate with domain experts to create domain-specific datasets that can be used to train models. We aim to create a set of tools that help users to collaborate with domain experts to create datasets that are representative of the domain. We aim to share the datasets openly on the hub and share the tools and skills to build these datasets.
🧑🏼🔬 If you are a domain expert, you can contribute by sharing your expertise and collaborating with us to create domain-specific datasets. We're working with user-friendly, easy-to-use applications that help you define the seed data and create the dataset. We're also working on tools that help you to annotate the dataset and improve the quality of the dataset.
🧑🏻🔧 If you are an (inspiring) Machine Learning engineer, you can set up the project and its tools. You can run the synthetic data generation pipelines. And maybe even get around to training models.
We start by selecting a domain and finding collaborators who can help us to create the dataset.
🧑🏼🔬 If you are a domain expert, you could find an ML engineer to help you to create the dataset.
🧑🏻🔧 If you are an ML engineer, you could find a domain expert to help you to create the dataset.
🧑🚀 If you're both, you could start by defining the seed data and creating the dataset.
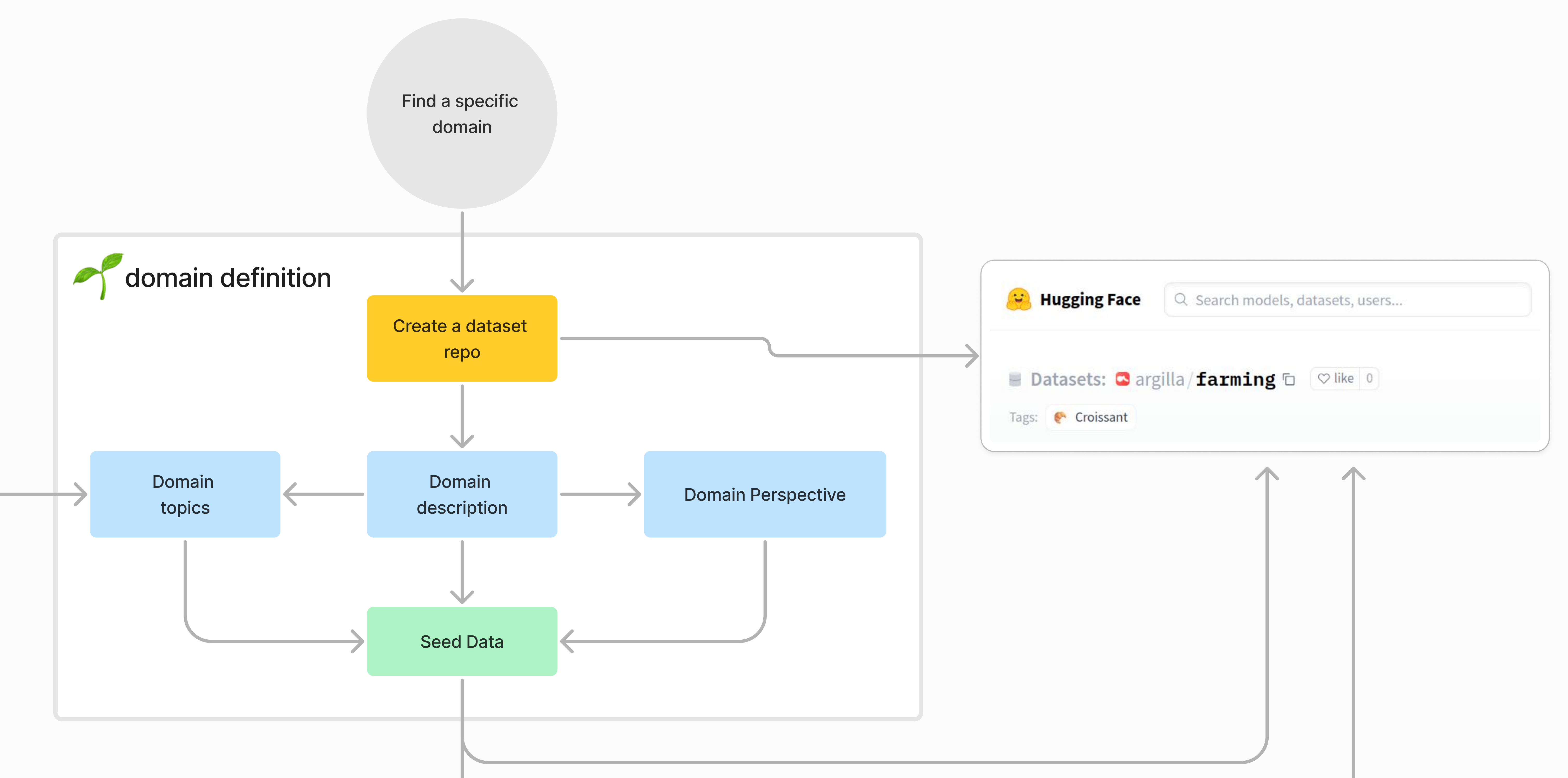
First you need o setup the project and its tools. For this, we use this application.
Next, we need to get the domain expert to define the seed data, which is used to create the dataset. Once the seed data is defined, we add it to the dataset repo.
Domain topics are the topics the domain expert wants to include in the dataset. For example, if the domain is farming, the domain topics could be "soil", "crops", "weather", etc.
Domain description is a description of the domain. For example, if the domain is farming, the domain description could be "Farming is the practice of cultivating crops and livestock for food, fiber, biofuel, medicinal plants, and other products used to sustain and enhance human life."
Domain perspectives are the perspectives the domain expert wants to include in the dataset. For example, if the domain is farming, the domain perspectives could be "farmer", "agricultural scientist", "agricultural economist", etc.
Next, we can move on to generating the dataset from the seed data.
To generate instructions and responses, you're going to need an endpoint. You can find compatible models from the Hugging Face Inference API here:
- 🔋Projects with sufficient resources could take advantage of LLama3 70b
- 🪫Projects with less resources could take advantage of LLama 3 8b
- 🍃Projects with even fewer resources could take advantage of Phi-2
Hugggingface Pro gives access to more compute resources.
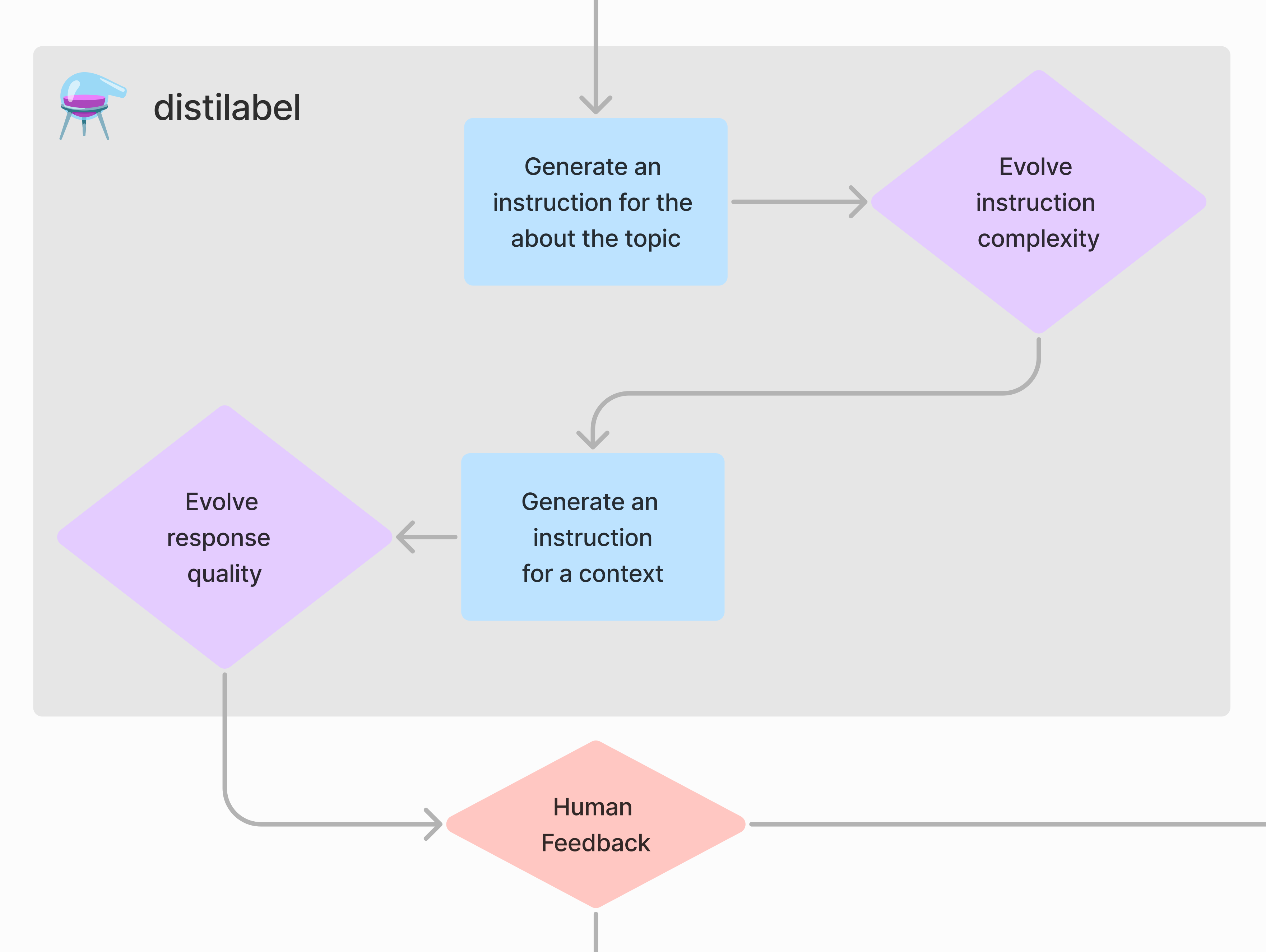
The pipeline takes the topic and perspective and generates instructions for the dataset, then the instructions are evolved by an LLM to create more instructions.
The pipeline takes the instructions and generates responses for the dataset, then the responses are evolved by an LLM to create higher quality responses.
Finally, the pipeline pushes the dataset to the hub and Argilla space. The domain expert can then refine the dataset by annotating the dataset and improving the quality of the dataset.
Here's a video guide that walks you through the process from end-to-end.
st.markdown("## Run the pipeline")
With the pipeline configuration define in the app and pushed to the dataset repo {hub_username}/{project_name}, you can run the pipeline via this repo.
You'll need to change directory, install dependencies, and log in to the Hugging Face Hub. You can do this by running the following commands:
cd data-is-better-together/domain-specific-datasets/distilabel_pipelines
pip install -r requirements.txt
huggingface-cli loginThen you can run the pipeline using the following command:
python domain_expert_pipeline.py {hub_username}/{project_name}""",app/: A streamlit app to help domain experts to define seed data like system prompt and topics, by creating an empty dataset on the hub.distilabel_pipelines/domain_expert_pipeline.py: The distilabel pipeline code that is used to create the dataset.scripts/: Adhoc scripts that we used to ease annotation with vector search.
Here are examples of the resources for our farming example:
- The seeding space: https://huggingface.co/spaces/argilla/domain-specific-seed for the domain expert.
- The demo dataset: https://huggingface.co/datasets/argilla/farming we've created
- The argilla space: https://huggingface.co/spaces/argilla/farming
- The pipeline code: https:/argilla-io/distilabel-workbench/tree/main/projects/farming