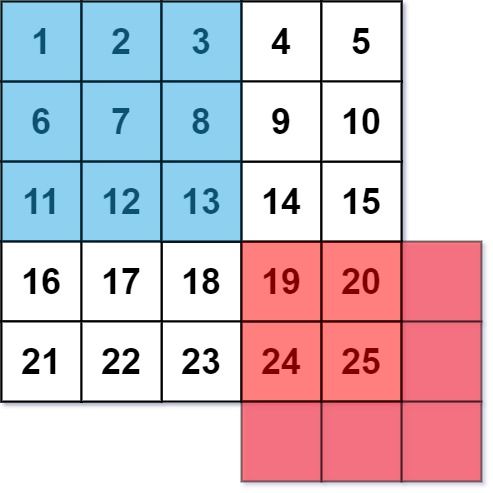
图像平滑器 是大小为 3 x 3 的过滤器,用于对图像的每个单元格平滑处理,平滑处理后单元格的值为该单元格的平均灰度。
每个单元格的 平均灰度 定义为:该单元格自身及其周围的 8 个单元格的平均值,结果需向下取整。(即,需要计算蓝色平滑器中 9 个单元格的平均值)。
如果一个单元格周围存在单元格缺失的情况,则计算平均灰度时不考虑缺失的单元格(即,需要计算红色平滑器中 4 个单元格的平均值)。
给你一个表示图像灰度的 m x n 整数矩阵 img ,返回对图像的每个单元格平滑处理后的图像 。
示例 1:
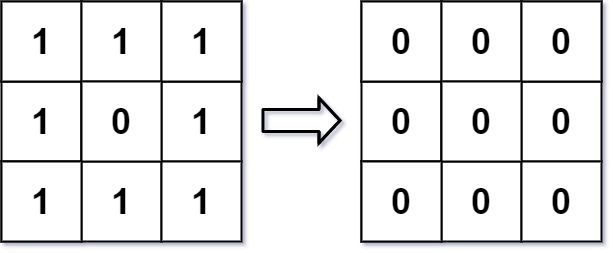
输入:img = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]] 输出:[[0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]] 解释: 对于点 (0,0), (0,2), (2,0), (2,2): 平均(3/4) = 平均(0.75) = 0 对于点 (0,1), (1,0), (1,2), (2,1): 平均(5/6) = 平均(0.83333333) = 0 对于点 (1,1): 平均(8/9) = 平均(0.88888889) = 0
示例 2:
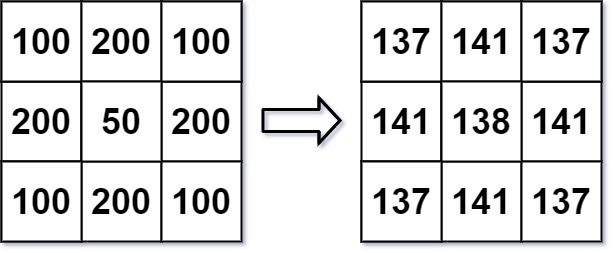
输入: img = [[100,200,100],[200,50,200],[100,200,100]] 输出: [[137,141,137],[141,138,141],[137,141,137]] 解释: 对于点 (0,0), (0,2), (2,0), (2,2): floor((100+200+200+50)/4) = floor(137.5) = 137 对于点 (0,1), (1,0), (1,2), (2,1): floor((200+200+50+200+100+100)/6) = floor(141.666667) = 141 对于点 (1,1): floor((50+200+200+200+200+100+100+100+100)/9) = floor(138.888889) = 138
提示:
m == img.lengthn == img[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= img[i][j] <= 255
class Solution:
def imageSmoother(self, img: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(img), len(img[0])
ans = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
s = cnt = 0
for x in range(i - 1, i + 2):
for y in range(j - 1, j + 2):
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n:
cnt += 1
s += img[x][y]
ans[i][j] = s // cnt
return ansclass Solution {
public int[][] imageSmoother(int[][] img) {
int m = img.length;
int n = img[0].length;
int[][] ans = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int s = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) {
for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) {
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
++cnt;
s += img[x][y];
}
}
}
ans[i][j] = s / cnt;
}
}
return ans;
}
}function imageSmoother(img: number[][]): number[][] {
const m = img.length;
const n = img[0].length;
const locations = [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 0],
[-1, 1],
[0, -1],
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, -1],
[1, 0],
[1, 1],
];
const res = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
res.push([]);
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
let sum = 0;
let count = 0;
for (const [y, x] of locations) {
if ((img[i + y] || [])[j + x] != null) {
sum += img[i + y][j + x];
count++;
}
}
res[i].push(Math.floor(sum / count));
}
}
return res;
}impl Solution {
pub fn image_smoother(img: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let m = img.len();
let n = img[0].len();
let locations = [
[-1, -1],
[-1, 0],
[-1, 1],
[0, -1],
[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, -1],
[1, 0],
[1, 1],
];
let mut res = vec![];
for i in 0..m {
res.push(vec![]);
for j in 0..n {
let mut sum = 0;
let mut count = 0;
for [y, x] in locations.iter() {
let i = i as i32 + y;
let j = j as i32 + x;
if i < 0 || i == m as i32 || j < 0 || j == n as i32 {
continue;
}
count += 1;
sum += img[i as usize][j as usize];
}
res[i].push(sum / count);
}
}
res
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> imageSmoother(vector<vector<int>>& img) {
int m = img.size(), n = img[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ans(m, vector<int>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int s = 0, cnt = 0;
for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) {
for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) {
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n) continue;
++cnt;
s += img[x][y];
}
}
ans[i][j] = s / cnt;
}
}
return ans;
}
};func imageSmoother(img [][]int) [][]int {
m, n := len(img), len(img[0])
ans := make([][]int, m)
for i, row := range img {
ans[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range row {
s, cnt := 0, 0
for x := i - 1; x <= i+1; x++ {
for y := j - 1; y <= j+1; y++ {
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n {
cnt++
s += img[x][y]
}
}
}
ans[i][j] = s / cnt
}
}
return ans
}